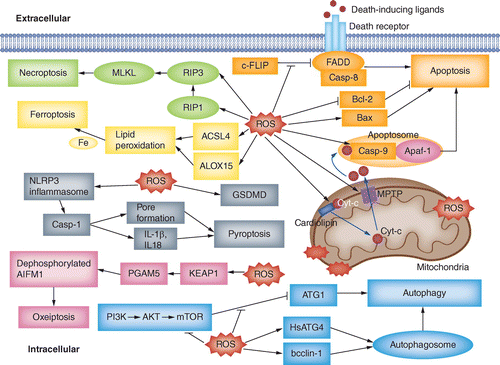
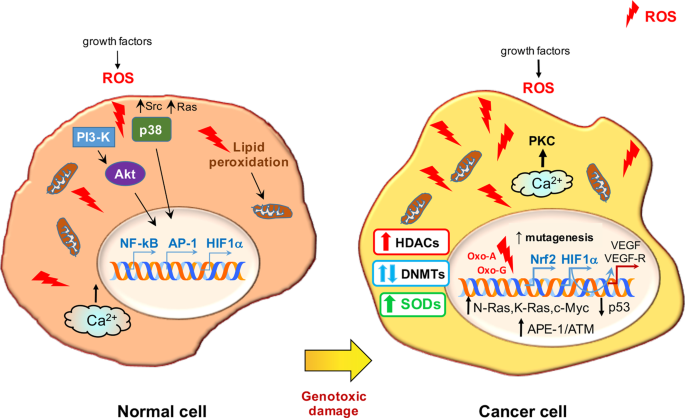
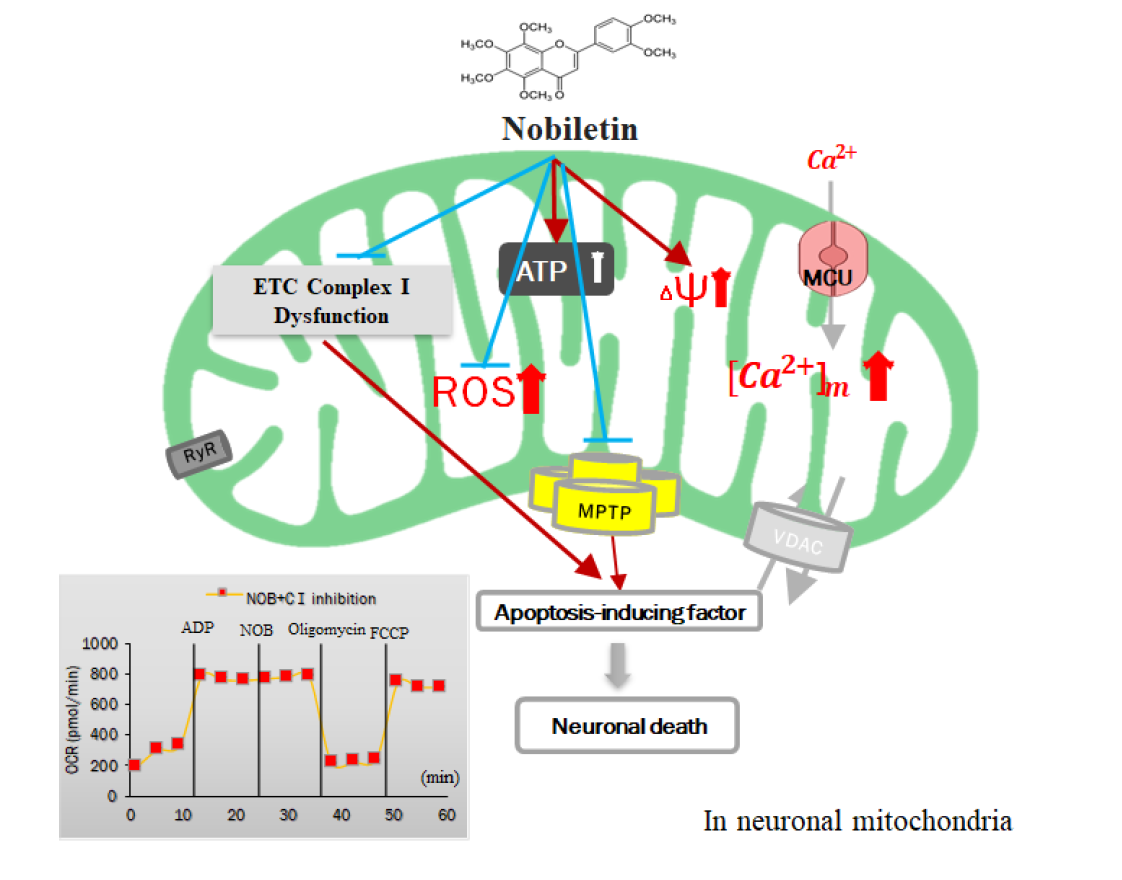
Cellular Thiols and Reactive Oxygen Species in Drug-Induced Apoptosis | Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics

Aflatoxin B1 impairs mitochondrial functions, activates ROS generation, induces apoptosis and involves Nrf2 signal pathway in primary broiler hepatocytes - Liu - 2016 - Animal Science Journal - Wiley Online Library

A reactive oxygen species activation mechanism contributes to Sophoridine-induced apoptosis in rat liver BRL-3A cells - ScienceDirect
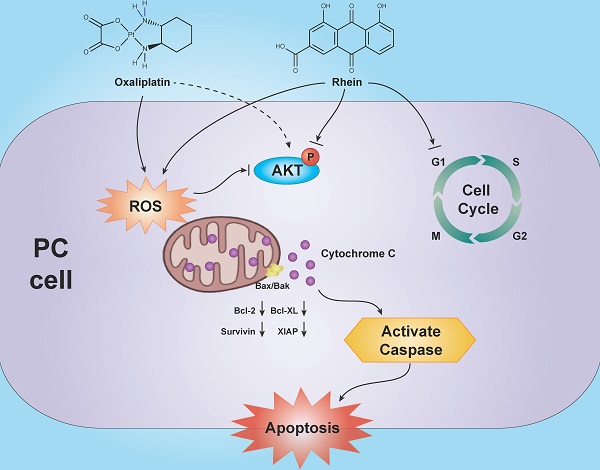
Inhibition of PI3K/AKT signaling via ROS regulation is involved in Rhein-induced apoptosis and enhancement of oxaliplatin sensitivity in pancreatic cancer cells
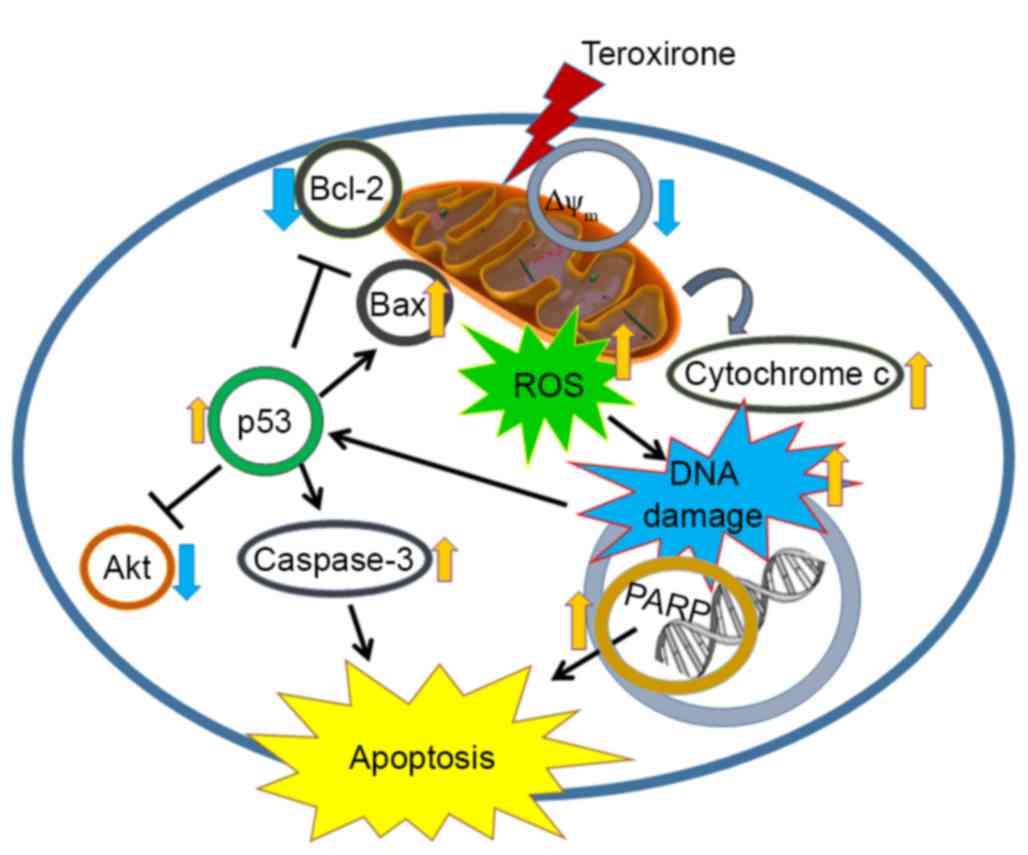
Reactive oxygen species-driven mitochondrial injury induces apoptosis by teroxirone in human non-small cell lung cancer cells

ROS mediated apoptotic pathways in primary effusion lymphoma: Comment on induction of apoptosis by Shikonin through ROS-mediated intrinsic and extrinsic pathways in primary effusion lymphoma | Semantic Scholar

Reactive Oxygen Species Induced by Bile Acid Induce Apoptosis and Protect Against Necrosis in Pancreatic Acinar Cells - Gastroenterology

ROS induced apoptosis. Schematic diagram of PCB influences ROS induced... | Download Scientific Diagram
N-Acetyl Cysteine Depletes Reactive Oxygen Species and Prevents Dental Monomer-Induced Intrinsic Mitochondrial Apoptosis In Vitro in Human Dental Pulp Cells | PLOS ONE
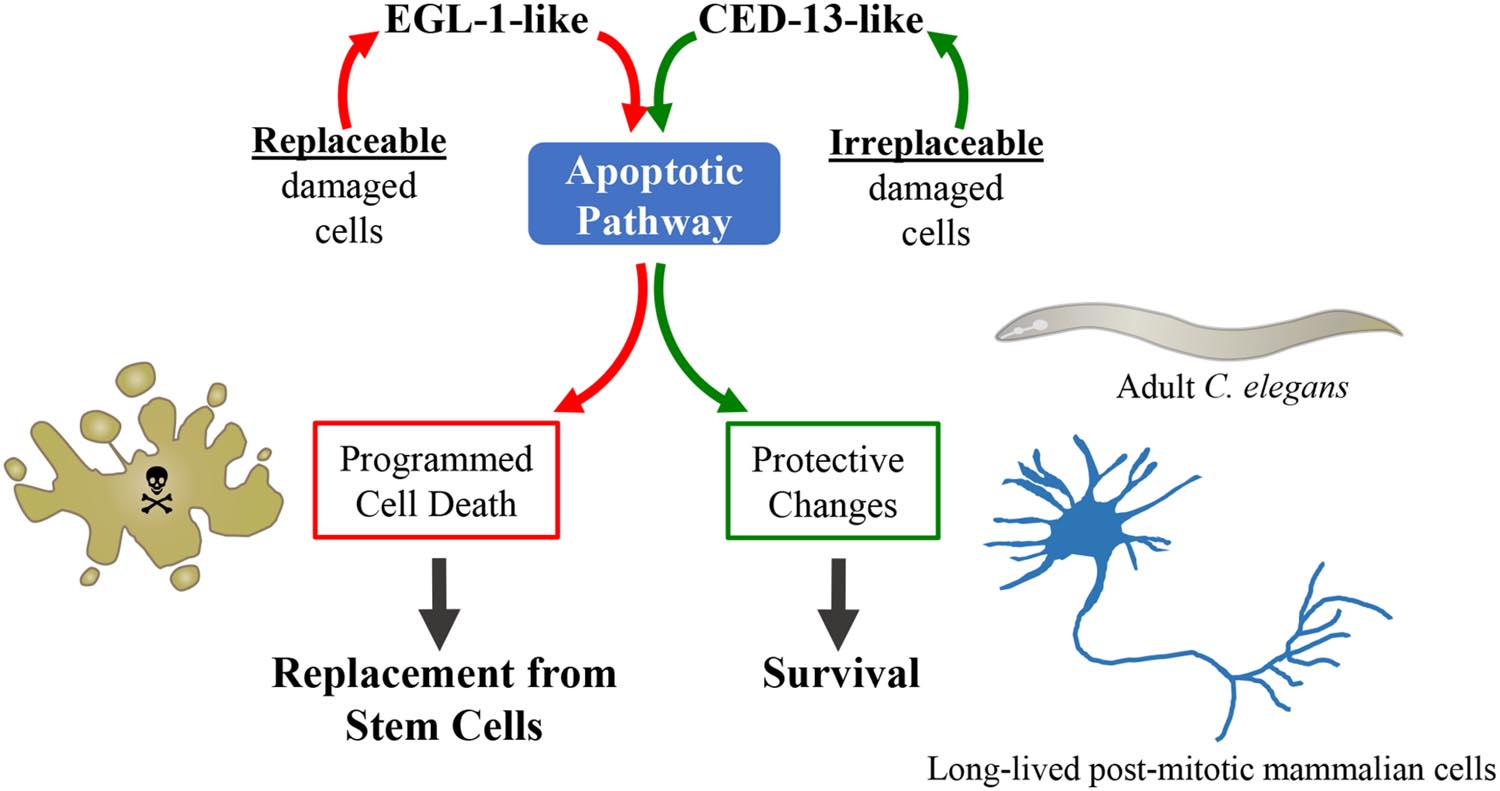
Frontiers | Mitochondrial ROS and the Effectors of the Intrinsic Apoptotic Pathway in Aging Cells: The Discerning Killers!

Marine Drugs | Free Full-Text | The Marine Fungal Metabolite, Dicitrinone B, Induces A375 Cell Apoptosis through the ROS-Related Caspase Pathway | HTML
Auranofin induces apoptosis by ROS-mediated ER stress and mitochondrial dysfunction and displayed synergistic lethality with piperlongumine in gastric cancer | Oncotarget
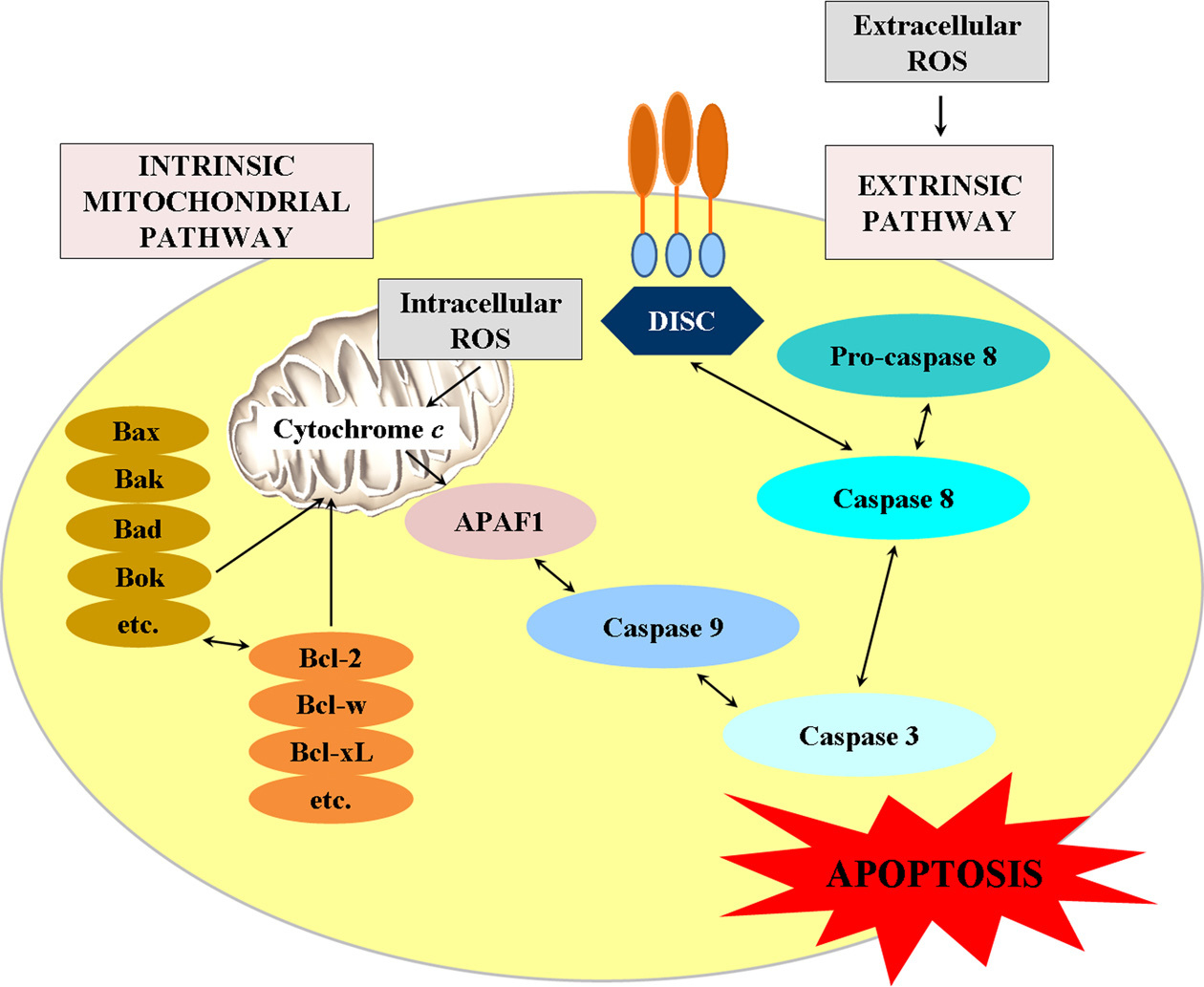
Overproduction of reactive oxygen species – obligatory or not for induction of apoptosis by anticancer drugs - Chinese Journal of Cancer Research

Figure 6 | Gallic Acid Induces a Reactive Oxygen Species-Provoked c-Jun NH2-Terminal Kinase-Dependent Apoptosis in Lung Fibroblasts
Novel camphor-based pyrimidine derivatives induced cancer cell death through a ROS-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis pathway - RSC Advances (RSC Publishing)
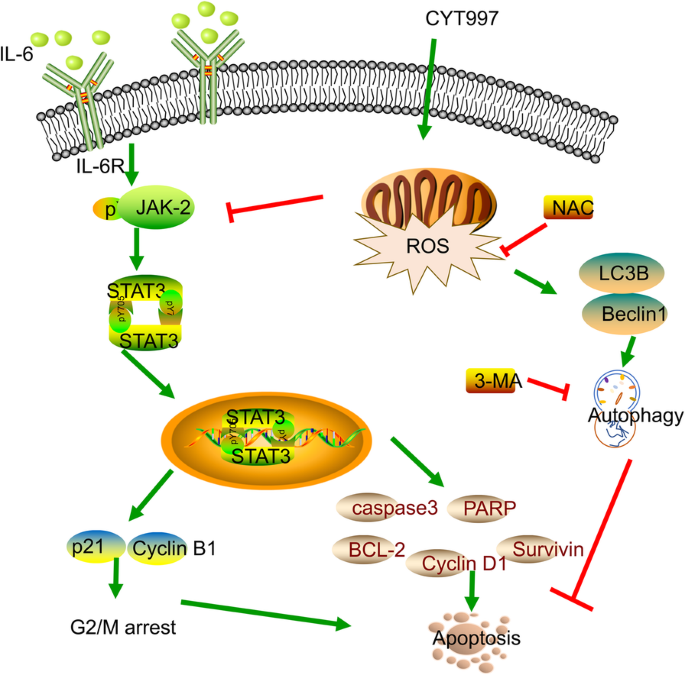
Mitochondrial ROS accumulation inhibiting JAK2/STAT3 pathway is a critical modulator of CYT997-induced autophagy and apoptosis in gastric cancer | Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research | Full Text